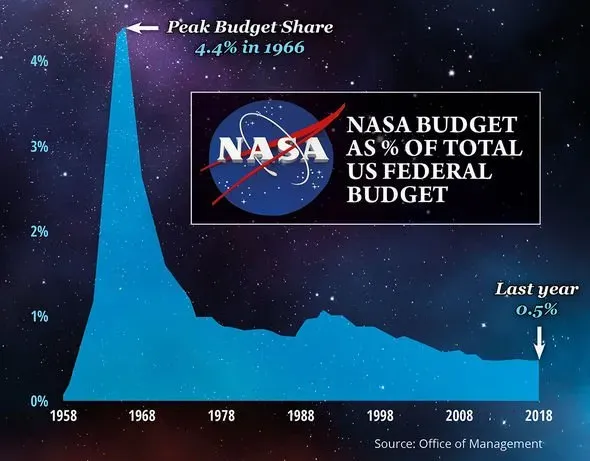
Currently, NASA budget cuts have become a hot topic of discussion as the Trump administration proposes to trim approximately $6 billion from the agency’s overall funding. This proposed NASA funding reduction not only seeks to redirect $1 billion towards Mars-focused missions but also raises concerns about the agency’s long-term capabilities. With significant budgetary constraints on the horizon, NASA acting administrator Janet Petro emphasizes the need for resilience among employees as they prepare for the potential downsizing of missions and workforce. The restructuring aims to prioritize initiatives aligning with commercial interests, particularly those driven by SpaceX and its ambitious Mars plans. As the debate around NASA budget 2025 continues, stakeholders are left to ponder the future of America’s space exploration endeavors.
The discourse surrounding reductions in NASA’s financial resources highlights the ongoing debate about the future of space exploration. Changes to funding allocations have sparked significant concern within the aerospace community, particularly in light of proposed budgetary cuts and their impact on missions aimed at interplanetary exploration. As NASA braces for potential operational changes and strategic realignments, many wonder how these adjustments will affect national priorities in space. The call for increased investment in Mars-related projects demonstrates a shifting focus, echoing the aspirations of private entities like SpaceX. Ultimately, the reallocation of funds within NASA will shape the landscape of space missions for years to come, underlining the necessity for a cohesive vision that balances exploration with fiscal responsibility.
Trump’s NASA Budget Cuts: A Shift in Priorities
The Trump administration’s proposal to cut approximately $6 billion from the NASA budget represents a significant shift in national priorities regarding space exploration. These reductions are not merely numbers on a ledger; they reflect a broader strategic realignment focused on Mars-focused missions. With $1 billion specially allocated to these initiatives, the administration aims to streamline operations while still fostering ambitions tied to interplanetary travel, showcasing a distinct preference for projects that promise immediate, attention-grabbing results.
Acting NASA administrator Janet Petro’s communication to the agency’s employees indicates that these budget cuts will necessitate tough decisions, affecting everything from workforce reductions to terminating multiple existing missions. This drastic trimming can result in lost opportunities for research and technological development, particularly in areas such as Earth and space science, that may have long-term benefits for humanity.
The Implications of NASA Funding Reduction on Future Missions
With NASA facing a funding reduction of about 25%, the ramifications for future space missions are multifaceted. Projects that were once deemed essential are at risk of being shelved or significantly limited, which raises concerns about the long-term goals of the U.S. space program. Missions associated with the Artemis program, for lunar exploration, and the Mars Sample Return program are among those being scaled back, potentially hindering the U.S.’s competitive edge in the space race.
Moreover, this funding reduction may impact collaborative efforts with private companies like SpaceX, which is actively working on its Mars plan. As NASA looks to streamline its budget, the agency’s partnerships with aerospace leaders could become critical in maintaining progress on ambitious goals, albeit under a tighter fiscal framework. This dynamic underscores the ongoing tension between governmental budget constraints and the aspirations of private enterprises in space exploration.
Adapting to Change: NASA’s Strategy for Mars-focused Missions
Despite the challenges posed by significant budget cuts, NASA is realigning its strategy towards Mars-focused missions. By investing $1 billion into these programs, the agency appears to be committing to its long-term objectives in planetary exploration, an area where public and private interests align. This move also resonates with the ambitions set forth by SpaceX and its CEO Elon Musk, who has voiced aspirations to expedite human travel to Mars.
This commitment presents an opportunity for NASA to innovate under constraint, leveraging private sector advancements while possibly rethinking or repurposing existing technologies for Mars missions. The collaboration may lead to new partnerships and funding avenues, allowing NASA to pursue interplanetary exploration with a refreshed focus. However, the consequences of budget cuts could ultimately shape the pace and scope of achieving these ambitious goals.
Streamlining Operations: NASA’s Workforce Challenges
As part of the proposed lean budget approach, NASA plans to streamline its workforce, which raises concerns within the agency. Reductions in staff may impact not only morale but also the breadth of expertise available to drive innovative projects. NASA’s success has historically been built on a robust team capable of tackling the intricate challenges of space exploration; thus, scaling down this workforce could lead to inefficiencies and delays in mission timelines.
Furthermore, the call for resilience among employees reflects the current climate of uncertainty regarding funding and future projects. The challenge lies not just in adjusting existing personnel numbers but also in maintaining high levels of motivation and productivity during a period marked by change and limitation. Employee adaptability will be crucial as NASA navigates through these tough operational shifts while striving to maintain its reputation as a leader in space research.
Mars Exploration: The End of Blue Sky Programs?
With the significant cuts to NASA’s discretionary budget outlined, it is clear that some of the agency’s more ambitious ‘blue sky’ programs may be curtailed. This has sparked debates about the effectiveness of government spending on exploratory science and whether such efforts should be prioritized over immediate, practical applications. The push to focus on Mars exploration amidst budget cuts may indicate a strategy that prioritizes public excitement and private engagement over a more comprehensive scientific approach.
As NASA moves forward with truncated goals, the powers of public-private partnerships come to the forefront. Companies like SpaceX may fill the gaps left by budget reductions, provided that their visions align with the goals of NASA’s initiatives. The future landscape of space exploration may hinge on this collaborative dynamic, creating a new model as considerations shift towards less reliance on traditional funding structures.
Financial Overview: Understanding NASA’s Budget 2025
In evaluating NASA’s proposed budget for 2025, it is essential to dissect the allocations and their intended impacts on mission outputs. With substantial reductions outlined, particularly focusing on civilian and scientific research components of the budget, stakeholders within the space community are left to ponder the future implications. The drastic cuts necessitate a rethinking of what NASA can accomplish, leading to questions about its capacity to meet national and international space exploration objectives.
The contrasting priorities highlighted in the budget also suggest a shift from a comprehensive exploration policy to a reactionary approach that responds to governmental directives. As funding for programs like moon landings and Mars missions increase, the overall vision may become fragmented, risking important long-term scientific endeavors that require consistent investment. Understanding NASA’s budget landscape will be crucial for stakeholders looking to participate in its ambitious plans.
Retirement of Key Programs: The Future of Space Exploration
The proposed retirement of landmark initiatives such as the Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft illustrates a fraught transition within NASA’s strategic direction. These cancellations, alongside ending the Gateway program, signify a foundational shift away from previously adopted long-term space exploration frameworks. The consequences may lead to a narrowing of scope in human spaceflight endeavors, making the ambitious goal of reaching Mars appear increasingly distant.
However, with this reduction in traditional programs, there is an opportunity for NASA to embrace innovation. By reallocating resources towards groundbreaking technologies and partnerships with emerging companies, the agency might find new pathways for exploration. The challenge will lie in ensuring that essential missions are not lost in the shuffle of a rapidly changing administrative agenda while advancing toward SpaceX’s Mars ambitions.
Collaborative Future: NASA and Private Sector in Space
The intersection of government space initiatives with private sector ambitions signals a pivotal moment in the future of space exploration. The collaboration between NASA and companies like SpaceX represents an evolving landscape in which traditional boundaries are blurred, leading to more dynamic and innovative mission planning. As NASA adapts to budget constraints, these partnerships will be foundational to mitigating the impacts of reduced funding on operational capabilities.
Creating a synergy with private entities also presents opportunities for shared technological advancements, cost efficiencies, and faster project timelines. However, this must be approached cautiously, as reliance on private funding and priorities can shift the mission focus away from scientific discovery towards commercial interests. Ensuring that NASA maintains its core mission while embracing collaboration will be key to its sustained success in an increasingly competitive space landscape.
Navigating the Future: NASA’s Response to Budget Constraints
As NASA navigates through potential budget cuts that could alter its course significantly, the agency’s response will determine its relevance in upcoming years. The proposed budget for 2025 may require a re-imagination of existing missions and a pivot towards ensuring that the emphasis remains on exploratory endeavors like Mars missions. The necessity for fiscal accountability may spur NASA to develop more innovative approaches, leveraging technology and collaboration to maintain momentum.
However, a clear communication strategy will be vital in articulating the importance of these changes not only to the agencies involved but also to the public. Transparency about the impacts of budget cuts and the realignment of strategic goals will be crucial in developing stakeholder buy-in, ensuring continued support for NASA’s objectives in the face of financial scrutiny. The agency’s adaptability and vision will be tested as it seeks to uphold its legacy of innovation in the cosmos.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the implications of the Trump NASA budget cuts on Mars-focused missions?
The Trump NASA budget cuts involve a reduction of about $6 billion, while reallocating $1 billion specifically for Mars-focused missions. This shift showcases a commitment to advancing Mars exploration, which aligns with private initiatives like SpaceX’s Mars plan. However, the budget cuts may lead to reduced funding for other space science initiatives that support Mars missions.
How will NASA budget cuts impact the agency’s operations in 2025?
NASA budget cuts in 2025 are projected to reduce the agency’s funding by approximately 25%, prompting the need for streamlining operations. This will affect workforce sizes, facility maintenance, and scientific missions, potentially leading to the termination of several programs, including some key Earth and space science initiatives.
What is the future of NASA funding reduction under the current administration?
Under the Trump administration, NASA funding reduction is seen as a necessity for fiscal responsibility, with significant emphasis on Mars-focused initiatives. Despite the cuts, the budget still allocates over $7 billion for moon exploration and introduces more than $1 billion for Mars programs, indicating a strategic shift rather than a complete withdrawal from ambitious space exploration.
What does NASA’s budget 2025 propose for Mars missions?
NASA’s budget for 2025 proposes a focused investment of $1 billion towards Mars missions, signifying a priority on Mars exploration despite broader funding reductions. This budget adjustment appears to support ongoing partnerships with private companies like SpaceX that share the goal of reaching Mars, essential for the long-term vision of human exploration in the solar system.
How will the Trump NASA budget cuts affect SpaceX’s plans for Mars colonization?
The Trump NASA budget cuts may complement SpaceX’s Mars plan by prioritizing funding for Mars-focused missions, even as NASA reduces funding elsewhere. SpaceX, with its Starship rocket, remains positioned as a leader in Mars exploration, indicating that budget cuts might inadvertently benefit private sector initiatives that are aligned with NASA’s goals.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Trump’s proposed budget cuts totaling $6 billion for NASA. |
| $1 billion is earmarked for Mars-focused missions to align with SpaceX’s ambitions. |
| NASA will need to streamline operations, including workforce and IT services, to adapt to the budget cuts. |
| The budget cut proposes a 25% reduction in NASA’s funding. |
| Significant cuts will affect Earth science, space science, and mission support divisions. |
| NASA is focusing on moon exploration with over $7 billion allocated while cutting other missions. |
| The SLS rocket, Orion spacecraft, and Gateway programs are among those set for retirement under this budget. |
Summary
NASA budget cuts have raised concerns as the Trump administration proposes a $6 billion reduction while shifting focus towards Mars exploration. This reallocation reflects a strategic pivot towards ambitious space missions, particularly with the increasing involvement of private companies like SpaceX. While these cuts pose challenges, NASA is committed to remain resilient and efficient in the face of these fiscal constraints.